Class GridBagLayout
- java.lang.Object
-
- java.awt.GridBagLayout
-
- All Implemented Interfaces:
- LayoutManager, LayoutManager2, java.io.Serializable
public class GridBagLayout extends java.lang.Object implements LayoutManager2, java.io.SerializableTheGridBagLayoutclass is a flexible layout manager that aligns components vertically, horizontally or along their baseline without requiring that the components be of the same size. EachGridBagLayoutobject maintains a dynamic, rectangular grid of cells, with each component occupying one or more cells, called its display area.Each component managed by a
GridBagLayoutis associated with an instance ofGridBagConstraints. The constraints object specifies where a component's display area should be located on the grid and how the component should be positioned within its display area. In addition to its constraints object, theGridBagLayoutalso considers each component's minimum and preferred sizes in order to determine a component's size.The overall orientation of the grid depends on the container's
ComponentOrientationproperty. For horizontal left-to-right orientations, grid coordinate (0,0) is in the upper left corner of the container with x increasing to the right and y increasing downward. For horizontal right-to-left orientations, grid coordinate (0,0) is in the upper right corner of the container with x increasing to the left and y increasing downward.To use a grid bag layout effectively, you must customize one or more of the
GridBagConstraintsobjects that are associated with its components. You customize aGridBagConstraintsobject by setting one or more of its instance variables:GridBagConstraints.gridx,GridBagConstraints.gridy- Specifies the cell containing the leading corner of the component's
display area, where the cell at the origin of the grid has address
gridx = 0,gridy = 0. For horizontal left-to-right layout, a component's leading corner is its upper left. For horizontal right-to-left layout, a component's leading corner is its upper right. UseGridBagConstraints.RELATIVE(the default value) to specify that the component be placed immediately following (along the x axis forgridxor the y axis forgridy) the component that was added to the container just before this component was added. GridBagConstraints.gridwidth,GridBagConstraints.gridheight- Specifies the number of cells in a row (for
gridwidth) or column (forgridheight) in the component's display area. The default value is 1. UseGridBagConstraints.REMAINDERto specify that the component's display area will be fromgridxto the last cell in the row (forgridwidth) or fromgridyto the last cell in the column (forgridheight). UseGridBagConstraints.RELATIVEto specify that the component's display area will be fromgridxto the next to the last cell in its row (forgridwidthor fromgridyto the next to the last cell in its column (forgridheight). GridBagConstraints.fill- Used when the component's display area
is larger than the component's requested size
to determine whether (and how) to resize the component.
Possible values are
GridBagConstraints.NONE(the default),GridBagConstraints.HORIZONTAL(make the component wide enough to fill its display area horizontally, but don't change its height),GridBagConstraints.VERTICAL(make the component tall enough to fill its display area vertically, but don't change its width), andGridBagConstraints.BOTH(make the component fill its display area entirely). GridBagConstraints.ipadx,GridBagConstraints.ipady- Specifies the component's internal padding within the layout,
how much to add to the minimum size of the component.
The width of the component will be at least its minimum width
plus
ipadxpixels. Similarly, the height of the component will be at least the minimum height plusipadypixels. GridBagConstraints.insets- Specifies the component's external padding, the minimum amount of space between the component and the edges of its display area.
GridBagConstraints.anchor- Specifies where the component should be positioned in its display area.
There are three kinds of possible values: absolute, orientation-relative,
and baseline-relative
Orientation relative values are interpreted relative to the container's
ComponentOrientationproperty while absolute values are not. Baseline relative values are calculated relative to the baseline. Valid values are: GridBagConstraints.NORTHGridBagConstraints.SOUTHGridBagConstraints.WESTGridBagConstraints.EASTGridBagConstraints.NORTHWESTGridBagConstraints.NORTHEASTGridBagConstraints.SOUTHWESTGridBagConstraints.SOUTHEASTGridBagConstraints.CENTER(the default)GridBagConstraints.PAGE_STARTGridBagConstraints.PAGE_ENDGridBagConstraints.LINE_STARTGridBagConstraints.LINE_ENDGridBagConstraints.FIRST_LINE_STARTGridBagConstraints.FIRST_LINE_ENDGridBagConstraints.LAST_LINE_STARTGridBagConstraints.LAST_LINE_ENDGridBagConstraints.BASELINEGridBagConstraints.BASELINE_LEADINGGridBagConstraints.BASELINE_TRAILINGGridBagConstraints.ABOVE_BASELINEGridBagConstraints.ABOVE_BASELINE_LEADINGGridBagConstraints.ABOVE_BASELINE_TRAILINGGridBagConstraints.BELOW_BASELINEGridBagConstraints.BELOW_BASELINE_LEADINGGridBagConstraints.BELOW_BASELINE_TRAILINGGridBagConstraints.weightx,GridBagConstraints.weighty- Used to determine how to distribute space, which is
important for specifying resizing behavior.
Unless you specify a weight for at least one component
in a row (
weightx) and column (weighty), all the components clump together in the center of their container. This is because when the weight is zero (the default), theGridBagLayoutobject puts any extra space between its grid of cells and the edges of the container.
Absolute Values
Orientation Relative Values
Baseline Relative Values
Each row may have a baseline; the baseline is determined by the components in that row that have a valid baseline and are aligned along the baseline (the component's anchor value is one of
BASELINE,BASELINE_LEADINGorBASELINE_TRAILING). If none of the components in the row has a valid baseline, the row does not have a baseline.If a component spans rows it is aligned either to the baseline of the start row (if the baseline-resize behavior is
CONSTANT_ASCENT) or the end row (if the baseline-resize behavior isCONSTANT_DESCENT). The row that the component is aligned to is called the prevailing row.The following figure shows a baseline layout and includes a component that spans rows:

- A panel that starts in row 0 and ends in row 1. The panel
has a baseline-resize behavior of
CONSTANT_DESCENTand has an anchor ofBASELINE. As the baseline-resize behavior isCONSTANT_DESCENTthe prevailing row for the panel is row 1. - Two buttons, each with a baseline-resize behavior of
CENTER_OFFSETand an anchor ofBASELINE.
Components positioned using one of the baseline-relative values resize differently than when positioned using an absolute or orientation-relative value. How components change is dictated by how the baseline of the prevailing row changes. The baseline is anchored to the bottom of the display area if any components with the same prevailing row have a baseline-resize behavior of
CONSTANT_DESCENT, otherwise the baseline is anchored to the top of the display area. The following rules dictate the resize behavior:- Resizable components positioned above the baseline can only grow as tall as the baseline. For example, if the baseline is at 100 and anchored at the top, a resizable component positioned above the baseline can never grow more than 100 units.
- Similarly, resizable components positioned below the baseline can only grow as high as the difference between the display height and the baseline.
- Resizable components positioned on the baseline with a
baseline-resize behavior of
OTHERare only resized if the baseline at the resized size fits within the display area. If the baseline is such that it does not fit within the display area the component is not resized. - Components positioned on the baseline that do not have a
baseline-resize behavior of
OTHERcan only grow as tall asdisplay height - baseline + baseline of component.
The following figures show ten components (all buttons) managed by a grid bag layout. Figure 2 shows the layout for a horizontal, left-to-right container and Figure 3 shows the layout for a horizontal, right-to-left container.
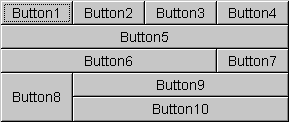
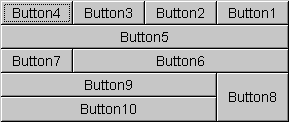
Figure 2: Horizontal, Left-to-Right Figure 3: Horizontal, Right-to-Left Each of the ten components has the
fillfield of its associatedGridBagConstraintsobject set toGridBagConstraints.BOTH. In addition, the components have the following non-default constraints:- Button1, Button2, Button3:
weightx = 1.0 - Button4:
weightx = 1.0,gridwidth = GridBagConstraints.REMAINDER - Button5:
gridwidth = GridBagConstraints.REMAINDER - Button6:
gridwidth = GridBagConstraints.RELATIVE - Button7:
gridwidth = GridBagConstraints.REMAINDER - Button8:
gridheight = 2,weighty = 1.0 - Button9, Button 10:
gridwidth = GridBagConstraints.REMAINDER
Here is the code that implements the example shown above:
import java.awt.*; import java.util.*; import java.applet.Applet; public class GridBagEx1 extends Applet { protected void makebutton(String name, GridBagLayout gridbag, GridBagConstraints c) { Button button = new Button(name); gridbag.setConstraints(button, c); add(button); } public void init() { GridBagLayout gridbag = new GridBagLayout(); GridBagConstraints c = new GridBagConstraints(); setFont(new Font("SansSerif", Font.PLAIN, 14)); setLayout(gridbag); c.fill = GridBagConstraints.BOTH; c.weightx = 1.0; makebutton("Button1", gridbag, c); makebutton("Button2", gridbag, c); makebutton("Button3", gridbag, c); c.gridwidth = GridBagConstraints.REMAINDER; //end row makebutton("Button4", gridbag, c); c.weightx = 0.0; //reset to the default makebutton("Button5", gridbag, c); //another row c.gridwidth = GridBagConstraints.RELATIVE; //next-to-last in row makebutton("Button6", gridbag, c); c.gridwidth = GridBagConstraints.REMAINDER; //end row makebutton("Button7", gridbag, c); c.gridwidth = 1; //reset to the default c.gridheight = 2; c.weighty = 1.0; makebutton("Button8", gridbag, c); c.weighty = 0.0; //reset to the default c.gridwidth = GridBagConstraints.REMAINDER; //end row c.gridheight = 1; //reset to the default makebutton("Button9", gridbag, c); makebutton("Button10", gridbag, c); setSize(300, 100); } public static void main(String args[]) { Frame f = new Frame("GridBag Layout Example"); GridBagEx1 ex1 = new GridBagEx1(); ex1.init(); f.add("Center", ex1); f.pack(); f.setSize(f.getPreferredSize()); f.show(); } }
- Since:
- JDK1.0
- See Also:
GridBagConstraints,GridBagLayoutInfo,ComponentOrientation, Serialized Form
-
-
Methods Modifier and Type Method and Description 
addLayoutComponent 
 Adds the specified component to the layout, using the specified
Adds the specified component to the layout, using the specifiedconstraintsobject.
addLayoutComponent 
 Has no effect, since this layout manager does not use a per-component string.
Has no effect, since this layout manager does not use a per-component string.
adjustForGravity 
 Adjusts the x, y, width, and height fields to the correct values depending on the constraint geometry and pads.
Adjusts the x, y, width, and height fields to the correct values depending on the constraint geometry and pads.
AdjustForGravity 
 This method is obsolete and supplied for backwards compatability only; new code should call
This method is obsolete and supplied for backwards compatability only; new code should calladjustForGravityinstead.
arrangeGrid 
 Lays out the grid.
Lays out the grid.
ArrangeGrid 
 This method is obsolete and supplied for backwards compatability only; new code should call
This method is obsolete and supplied for backwards compatability only; new code should callarrangeGridinstead.
getConstraints 
 Gets the constraints for the specified component.
Gets the constraints for the specified component.
getLayoutAlignmentX 
 Returns the alignment along the x axis.
Returns the alignment along the x axis.
getLayoutAlignmentY 
 Returns the alignment along the y axis.
Returns the alignment along the y axis.
getLayoutDimensions 
 Determines column widths and row heights for the layout grid.
Determines column widths and row heights for the layout grid.
getLayoutInfo 
 Fills in an instance of
Fills in an instance ofGridBagLayoutInfofor the current set of managed children.
GetLayoutInfo 
 This method is obsolete and supplied for backwards compatability only; new code should call
This method is obsolete and supplied for backwards compatability only; new code should callgetLayoutInfoinstead.
getLayoutOrigin 
 Determines the origin of the layout area, in the graphics coordinate space of the target container.
Determines the origin of the layout area, in the graphics coordinate space of the target container.
getLayoutWeights 
 Determines the weights of the layout grid's columns and rows.
Determines the weights of the layout grid's columns and rows.
getMinSize 
 Figures out the minimum size of the master based on the information from
Figures out the minimum size of the master based on the information fromgetLayoutInfo.
GetMinSize 
 This method is obsolete and supplied for backwards compatability only; new code should call
This method is obsolete and supplied for backwards compatability only; new code should callgetMinSizeinstead.
invalidateLayout 
 Invalidates the layout, indicating that if the layout manager has cached information it should be discarded.
Invalidates the layout, indicating that if the layout manager has cached information it should be discarded.
layoutContainer 
 Lays out the specified container using this grid bag layout.
Lays out the specified container using this grid bag layout.
location 
 Determines which cell in the layout grid contains the point specified by
Determines which cell in the layout grid contains the point specified by(x, y).
lookupConstraints 
 Retrieves the constraints for the specified component.
Retrieves the constraints for the specified component.
maximumLayoutSize 
 Returns the maximum dimensions for this layout given the components in the specified target container.
Returns the maximum dimensions for this layout given the components in the specified target container.
minimumLayoutSize 
 Determines the minimum size of the
Determines the minimum size of theparentcontainer using this grid bag layout.
preferredLayoutSize 
 Determines the preferred size of the
Determines the preferred size of theparentcontainer using this grid bag layout.
removeLayoutComponent 
 Removes the specified component from this layout.
Removes the specified component from this layout.
setConstraints 
 Sets the constraints for the specified component in this layout.
Sets the constraints for the specified component in this layout.
toString 
 Returns a string representation of this grid bag layout's values.
Returns a string representation of this grid bag layout's values.